Popular Articles
- Herdox Supplement Facts
- Itching from Herpes? Learn How to Stop it
- Thirteen Herbs for Herpes
- Can You Get Rid of Herpes?
- Herpes Vitamin Supplements
- Stop Recurring Herpes Incidences
- 11 Tips to Manage Your Herpes Outbreak
- Vaccine for Herpes
- Water and Herpes- Does Water Spread It?
- Bleach and Herpes
- More Articles ...
 Herpes SymptomsIn This Article
We look at all of the symptoms of herpes, including both oral herpes and genital herpes symptoms.
One of the main reasons that herpes affects such a large percentage of the population is because many people fail to recognize the symptoms of herpes. Many people also think they have herpes, when they may have something else. In this article, we will examine the symptoms of both HSV-1 and HSV-2. Asymptomatic HerpesThe primary infection (the first infection after catching herpes) is generally the worst. However, 30 to 40% of all primary infections are asymptomatic, meaning that they cause no herpes symptoms at all. It's possible to develop symptoms during recurrent herpes outbreaks, but some people may never develop symptoms. As a result, it's possible to get herpes and spread herpes without any knowledge of an infection. HSV-2 – Genital Herpes Symptoms – Primary InfectionHSV-2 is generally regarded as genital herpes because that is where symptoms tend to be strongest, but it can be spread to the mouth if shedding occurs during oral sex. While primary infections may be asymptomatic, they are the most likely outbreak to cause significant herpes symptoms. Nevertheless, herpes may manifest itself in many different ways, and it's possible to experience any combination of the following herpes symptoms:
Not all those that get herpes will experience a fever. Yet fever is generally the first symptom of herpes. Fever occurs roughly 6 to 7 days after exposure to the herpes virus. Fever may also be accompanied by muscle ache, headache, malaise, and nausea similar to the flu or other illness.
Before any visible symptoms appear, herpes goes through what is known as the "prodromal phase." The word "prodrome" generally refers to any symptoms that occur before a disease manifests. In a way, they are the symptoms of the symptoms. The prodromal phase of the herpes virus occurs when the virus is in the process of duplicating. This duplication occurs when the virus is coming to the surface of the skin. The virus is literally multiplying itself in order to shed. During the prodromal phase, the skin within or around the vagina, or on the tip or shaft of the penis begins to tingle, as though being poked by pins and needles. Some people with HSV-2 experience itching or burning instead, though these are less common during the prodromal phase. Also, the prodromal phase may not be limited to the genital region. You may feel this tingling, itching, or burning on the buttocks or back down the leg. The prodromal phase usually lasts between 1 and 3 days, although for some people it is very brief. Like all herpes symptoms, not everyone suffering from herpes simplex 2 will experience the prodromal phase. During the prodromal phase, the herpes virus is very contagious.
Blisters are the most recognizable symptom of herpes and the one that makes it easier for doctors to diagnose a case of HSV.
Herpes blisters may look like a pimple, or they may look like a collection of ulcers. In most cases these sores pop and scab over. With genital herpes, the sores are usually found inside the cervix, on the labia or the skin surrounding the vagina. On men, the sores may appear on both the tip of the penis, shaft, scrotum or surrounding skin. Nearly all herpes sores become encrusted after 2 weeks. By the third week, the sore will generally disappear. Unless infected or scratched, herpes sores do not generally leave any scars.
HSV-2 is more contagious for women than men. One possible symptom associated with primary HSV-2 infections is vaginal discharge, along with accompanying pressure in the lower abdomen. There is no color of vaginal discharge associated with herpes. However, the sores within the vagina may rupture, and this could add a red/brown hue to the color of herpes discharge. Because vaginal discharge may also be caused by other types of infections, it's often a good idea to see a doctor.
Pain is a common herpes symptom. Sores caused by genital herpes can be very painful, and when they open up to the air and begin to crust over, the pain can be anywhere from mild to unbearable during your first outbreak. Open or closed, these blisters may cause pain. It's also possible to develop painful urination, especially in women. Urinating may irritate the blisters and cause extreme pain, and some blisters and herpes outbreaks cause inflammation that can make it difficult and painful to urinate.
Throughout the outbreak, one of the most common symptoms of herpes is itching. Itching is common in the prodromal phase and generally continues as the sores develop on the genitals.
Herpes may also be accompanied by a rash, in addition to the blisters. The rash increases the amount of itching experienced by the individual. Scratching should generally be avoided as it will often increase the amount of itching and irritation and possibly cause an infection. During a bad primary infection, all of these symptoms may be present. If the initial infection is not severe, it is still possible to experience all or some of these symptoms, with varying degrees of severity.
Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes that surround the spinal cord and the brain. 10% of all HSV-2 cases result in herpes meningitis, and the disorder is more common in women than men. Symptoms are similar to traditional meningitis and include sensitivity to light, vomiting, headache, and fever. Some of these symptoms may be indistinguishable from traditional primary infection symptoms. Herpes meningitis lasts for roughly 7 days and tends to fade without any long-term consequences. In very rare cases, herpes meningitis may be recurrent. This is known as "Mollaret Meningitis."
The herpes simplex virus rarely has any severe complications. One of the rarest complications is known as eczema herpeticum – an extremely rare herpes symptom that can be fatal, but can also be easily treated with antivirals if treatment is sought out early. Eczema herpaticum is most likely if the patient has pre-existing skin problems, and is more common in children. It presents itself as numerous bumps that often occur all over the body, rather than just at the site of the herpes outbreak. HSV-2 – Genital Herpes Symptoms – Recurrent InfectionOnce contracted, herpes cannot be cured. Herpes remains in the body attached to nerve cells, and on occasion rises to the surface in what is known as a "recurrence." Generally, the medical field only recognizes it as a recurrence when there are at least one or more of the common symptoms of herpes. As such, those that experience asymptomatic herpes are rarely considered going through "recurrences." Shedding is still possible even without herpes symptoms, so transmitting the disease to partner is still a concern. Recurrences also decrease over time. According to a study at the University of Hawaii, there appears to be, on average, roughly 1 or 2 fewer recurrences every 5 years after initially contracting HSV-2. Many doctors recommend suppressive therapy to reduce recurrences and supplements or medicine to reduce herpes symptoms. In general, recurrences tend to be weaker than initial infections by a wide margin, although this is less true in those that had asymptomatic infections. Some of the differences between primary and recurrent infections include:
Most other symptoms are the same, although the immune system may reduce the severity of all herpes symptoms over time in some patients. Are There Differences in Herpes Symptoms Between HSV-1 (Oral Herpes) and HSV-2?
There are very few differences between HSV-1 and HSV-2 in terms of symptoms. These include:
Otherwise, the symptoms of herpes simplex 1 and herpes symptoms 2 are identical – the only difference between them being the common location of infections. Managing Herpes SymptomsHerpes symptoms are commonly managed through anti-viral medications, topical creams, and supplements designed to reduce itching. Herpes may not be curable, but there are prevention strategies that can reduce recurrences, and methods of relieving some of the most disruptive symptoms, such as itching and pain. Sourceshttp://ije.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/4/698.full.pdf http://www.hawaii.edu/hivandaids/Clinical_Reactivation_of_Genital_HSV_Infection_Decreases_in_Freq_over_Time.pdf http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3033506
[+] Show All
|
||||
| Next Article: Herpes | How To Stop the Itch |





 Herpes is a highly contagious sexually transmitted disease. 21% of the population is infected with genital herpes, and as many as 67% of the population is infected with oral herpes.
Herpes is a highly contagious sexually transmitted disease. 21% of the population is infected with genital herpes, and as many as 67% of the population is infected with oral herpes.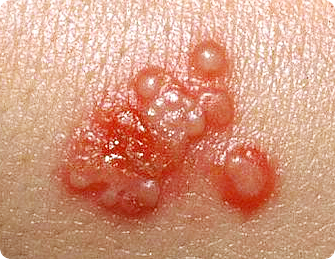 Herpes symptoms are unusual, in that blisters may occur in groups, or you may get only a single blister. They may be of different sizes and manifest in different ways.
Herpes symptoms are unusual, in that blisters may occur in groups, or you may get only a single blister. They may be of different sizes and manifest in different ways.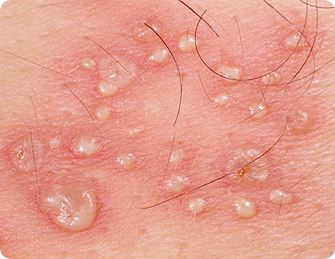 Different patients experience different levels of itching, but many describe itching as one of their most disruptive symptoms. Itching may occur at the site of the blisters or anywhere infected with herpes.
Different patients experience different levels of itching, but many describe itching as one of their most disruptive symptoms. Itching may occur at the site of the blisters or anywhere infected with herpes.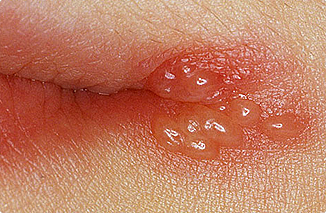 Generally, most people see HSV-1 as the "lesser" of the two viruses, since it typically affects the mouth, while HSV-2 affects the genitals. However, these two viruses are identical in symptoms, which is why those that get HSV-2 on their mouths or HSV-1 on their genitals see the same symptoms.
Generally, most people see HSV-1 as the "lesser" of the two viruses, since it typically affects the mouth, while HSV-2 affects the genitals. However, these two viruses are identical in symptoms, which is why those that get HSV-2 on their mouths or HSV-1 on their genitals see the same symptoms.