Popular Articles
- Thyax Supplement Facts
- Best Natural Thyroid Supplements
- Try THESE Instead of Synthroid
- T3 - Weight Loss
- Boost an Underactive Thyroid
- Product Review | Armour Thyroid
- Thyroid Health | How to Boost T3 and T4 Levels
- Thyroid Health | The Best Vitamins for Hypothyroidism
- Ginger and Weight Loss
- Best Weight Loss Supplements for Men and Women
- More Articles ...
 4 Hypothyroid DisordersIn This Article
Four common thyroid disorders and how they are treated.
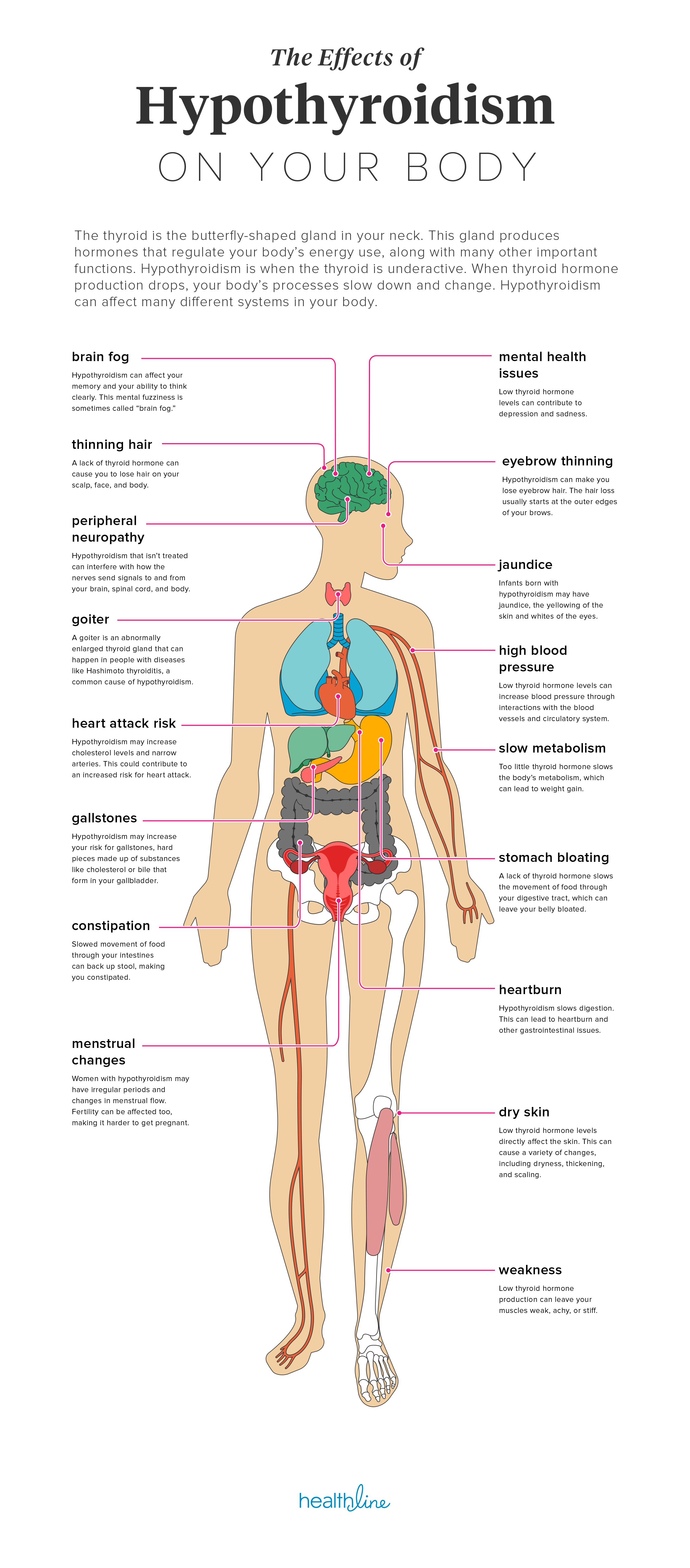
Gaining weight, difficulty paying attention, and lack of energy are all symptoms of a thyroid disorder. Hypothyroidism, or a lack of thyroid hormones, is a serious health condition with a variety of causes. This article will define 4 types of hypothyroidism, discuss causes and risk factors, list signs and symptoms, and offer treatment options.
Thyroid Disorder #1- Hashimoto's thyroiditisThe most common type of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis, an autoimmune thyroid disorder. Autoimmune diseases, commonly believed to be started by a bacterial or viral infection, cause the immune system to attack its own body. In Hashimoto's thyroiditis, the thyroid gland is the victim. Because the thyroid helps regulate the basal body metabolism, lack of the hormone affects the entire body- everything from appetite to body temperature. Thyroid Disorder #2- Postpartum hypothyroidismPostpartum hypothyroidism is a form of thyroiditis that occurs after giving birth. It is unfortunately misdiagnosed often, as many new mothers are generally fatigued. Postpartum hypothyroidism initially causes thyrotoxicosis (too much thyroid in the blood) and then hypothyroidism (too little hormone in the blood). The exact cause is unknown, but it is generally believed to be an autoimmune disease. There are several risk factors for developing it. Secondary hypothyroidism can remain in about 20 % of patients.
Infants born to mothers suffering from this disorder should be carefully monitored, as it may have affected their development as well. Lack of thyroid hormone in infants and children can have devastating effects. The presenting signs are different with adults as well. Medline Plus has more information on autoimmune diseases. Thyroid Disorder #3- ThyroiditisInflammation of the thyroid gland is known as thyroiditis. If caused by infection or trauma to the gland, it may be painful and tender. If the cause is autoimmune or iatrogenic, there is generally no pain associated with it.
Although these can occur in all ages and both sexes, women between 20-50 have the highest risk. If this disease does resolve, there is a risk that hypothyroidism can reoccur in later years. It is known that immune disorders, viruses, bacterial infections, and high fevers can cause this disorder. Thyroid Disorder #4 -Graves diseaseGraves disease (another autoimmune disease) causes hyperthyroidism, which can lead to hypothyroidism. Medications known to affect adversely the thyroid include amiodarone, lithium, and chemotherapy. Excessive amounts of iodine in the diet can contribute to thyroid disorders. Occasionally, a definitive cause cannot be found. Thyroid CancerThe incidence of thyroid cancer is coming down over time. Early inappropriate use of X-rays led to an increase, which is resolving as time passes. In the early to middle 20th century, doctors used high dose X-rays to treat children for enlarged tonsils, acne, and other issues affecting the head and neck. At one point in time, there was a commercial device used to measure feet that exposed people to radiation as well. Both of these are no longer done. This exposure can cause papillary or follicular thyroid cancer. Radioactive fallout also causes thyroid cancer. Atomic weapons testing, nuclear power plant accidents, and releases from weapons that produce atomic weapons are all sources of fallout. It is known that exposure to I-131 increases the risk of thyroid diseases, including cancer. Medullary thyroid cancer is genetic. The gene called RET, if altered, causes an extremely high percentage of people to develop that particular form of cancer. Doctors treating a person for this form of cancer may suggest that all family members be tested. If a family member has this form of cancer, others in your family are at higher risk for other types of cancer as well.
They reflect the changes occurring within the body due to the slowing of basal metabolism. In the early stages, hypothyroidism is easily missed. This is because the symptoms can be misdiagnosed, or considered to be a natural side effect of aging or other circumstances in life. Severe fatigue, weight gain, and increased sensitivity to cold are more noticeable than other symptoms. As the hormones continue to drop, slowed speech, low blood pressure, and pulse, hoarseness in the voice, and constipation are noted along with menstrual problems. The symptoms increase in severity, causing changes in the person's appearance- goiter may be present, dry-thick-coarse hair may occur, confusion and depression may be apparent. Thyroid Disorder TreatmentsTreatment of thyroid disorders depends on the cause. In postpartum hypothyroidism, all that may be needed is regular blood tests to be sure the gland is regaining its functions. Medications for pain, antibiotics for an infection, and steroids to reduce swelling and inflammation may also be prescribed, depending on symptoms. Synthetic thyroid hormones (such as Synthroid, Levoxyl, Levothroid, & Unithroid) are generally prescribed for hypothyroidism and large goiters, but there is a natural desiccated thyroid hormone (such as Armour) made from pig thyroids available. For thyroid cancer, surgery is the best treatment. This may be followed up with radiation to the thyroid if the surgery does not remove all thyroid tissue. Conventional medical treatment is necessary- homeopathic remedies, supplements (such as Magnesium, L Tyrosine, Zinc & Copper), thyroid products, and foods can help support treatment. Foods That May Cause Thyroid DisordersThere is considerable controversy in the medical community about the consumption of soy products. It has been reported that soy may interfere with the absorption of thyroid medications. There have been some studies that suggest this, but no definitive ones. This is not the only food or medication thought to interfere with thyroid medications. Here are some additional foods & supplements that may interfere with absorption:
If you do choose to include soy foods in your diet, be sure to wait for least four hours after taking the medication. Generally, the medication is taken on an empty stomach.
Vitamins and supplements are often suggested to help improve thyroid response. Fish oil helps decrease inflammation and stabilize the immune system. Ask your doctor before starting these, because they interact with blood thinners and make bleeding disorders worse. L-tyrosine is used by the thyroid to make thyroid hormone. DO NOT take this if you are taking thyroid replacement already, or if you suffer from hypertension or mania. Iodine supplements only help if the hypothyroidism is caused by a lack of iodine in the diet. Too much iodine can cause hypothyroidism. |
||||||||||||
| Next Article: Low T3 and T4 Levels? Boost it: Heres How... |