Learn about symptoms, medications, and treatments for thyroid disorders.
The Thyroid Gland is responsible for the metabolism rate of our body, as well as cell growth and regeneration. Most people have heard of thyroid disorders, and there are over 200 million people around the world that suffer from them.
Twenty-seven million of these people are Americans, and above half of the 27 million are undiagnosed. There are four main types of thyroid disorders and two of them are Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism.
Hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland is not producing or making enough thyroid hormones.
If there is a lack of supply of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream, the body’s metabolic rate drops as well causing a vast range of side effects.
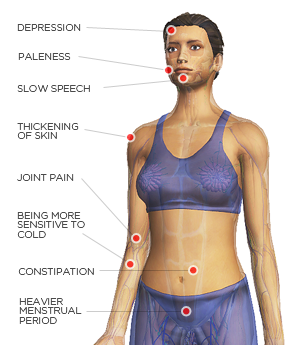
47 specific symptoms have been identified to be present in people suffering from low thyroid function, and here are some:
- Constipation
- Heavier menstrual period for women
- Paleness
- Depression
- Being more sensitive to cold
- Weakness
- Joint pain
- Brittle fingernails and/or hair
- Slow speech
- Decreased sense of smell or taste
- Puffy hands, face, or feet
- Thickening of skin
- Lethargy
The most common cause of hypothyroidism is the inflammation of the thyroid gland. And if that happens, it damages the cells of the gland.
The most common example of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Autoimmune thyroiditis - where the immune system of the body begins to attack the thyroid gland causing complications and damage to the gland itself.
Other things cause hypothyroidism. Usually, these causes are congenital or birth defects. It may also include cancer or tumor treatment to the neck which may directly affect or damage the thyroid gland. Surgery or the removal of a part of the thyroid gland, drug or medical intake, as well as other drugs used to treat hyperthyroidism can also take a toll on the body.
Some women develop “postpartum thyroiditis”, which occurs after a woman has given birth.
There is no way to prevent or stop Hypothyroidism, but it is curable. Once the symptoms start to manifest, visit your health care provider or physician and have yourself tested.
If the test and exam results show that the problem is hypothyroidism, your doctor or physician would prescribe TSH or Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone medicine such as Levothyroxine, Synthroid, or Unithroid.
Most of the time, the doctor will require you to start with a small dosage to avoid the possibility of side effects and other complications. Once you begin taking the medication, you should not stop taking it even if the symptoms of the disorder go away.
If you are taking prescription medication for hypothyroidism, you must make sure that you visit your doctor twice a year. This is so that you can have your thyroid hormone level measured. Never take TSH medicine with fiber supplements such as calcium, iron, multivitamins, antacids, aluminum hydroxide, or medicines or supplements that bind bile acids. Always consult your doctor in case you want to switch brands or try another kind of medication.
Lastly, if you’re having side effects due to medication, visit your doctor immediately.
Hyperthyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland produces too much of its hormones for a short (acute) or long (chronic) period of time.
The signs or symptoms are the following:
- Palpitations
- Over fatigue
- Sweatiness
- Rapid bowel movement
- Irritability
- Sudden paralysis
- Shortness of breath
- Nervousness
- Goiter
Hypothyroidism can be caused by several things – and they can be external such as the things we do or internal, which occur inside the body. The most common causes of hypothyroidism are as follows:
- Excessive iodine intake
- Thyroiditis or inflammation of the thyroid gland
- Abnormal release of TSH of the gland
- Grave’s disease
There are no known ways to prevent hyperthyroidism, but like hypothyroidism, it is manageable. The treatment for hyperthyroidism depends on the severity of the symptoms. Most of the time, Hyperthyroidism is treated with one or more of the following:
- Antithyroid medications
- Surgery to remove the thyroid
- Radioactive iodine
If you suffer from hypothyroidism, your doctor will assess the gravity of your condition and determine the best hypothyroidism treatment for you.






 Hypothyroidism Symptoms
Hypothyroidism Symptoms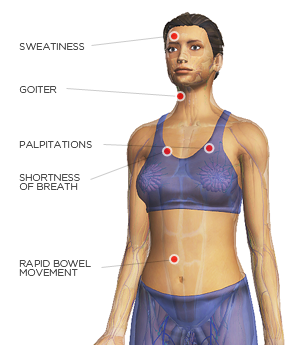 Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism